1. Yan LI, Zhen YAO, Zhen-hua CHEN, Shao-long QIU, Changchun ZENG, Kun CAO, “Rheological Evidence of Physical Cross-Links and Their Impact in Modified Polypropylene”, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013,52: 7758–7767(SCI/TOP期刊)
Abstract:This paper reports our investigation of the existence of physical cross-links in modified polypropylenes (PPs) containing long chain branches (LCBPPs) or amine moiety (PP-g-NH2). By varying the stoichiometric ratio of maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (PP-g-MAH) and ethylenediamine (EDA), a series of modified PPs with different degrees of branching and side-group polarities were prepared. Extensive rheological studies were conducted after baseline characterization of the chemical and molecular structures of these materials using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and size exclusion chromatography (SEC), respectively. The results strongly suggest the presence of physical cross-links in a majority of the materials studies herein, which significantly impacts their rheological behaviors. The physical cross-links can be argued to be in the form of phase-separated domains and hydrogen bonding, which has been reported in the literature.
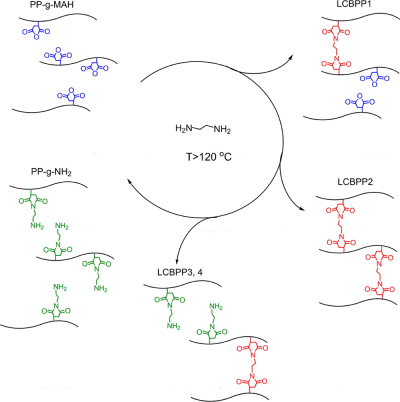
Illustrations of the Structural Differences among Modified PPs Prepared by Varying the Stoichiometric Ratio (R) of PP-g-MAH and Ethylenediamine (EDA)
2. Zhenhua CHEN, Changchun ZENG, Zhen YAO, Kun CAO, “Solid-State Foaming of Cyclic Olefin Copolymer by Carbon Dioxide”, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013,52: 9381–9396(SCI/TOP期刊)
Abstract:Solid-state foaming of cyclic olefin copolymer (COC, Topas 6017) using carbon dioxide (CO2) was investigated. Before the foaming experiment, the solubility of CO2 in the polymer at various saturation pressure (5–10 MPa) and saturation temperature (40 °C) was measured using the ex-situ gravimetric method. The effects of the saturation pressure, foaming temperature, and foaming time on the foam structure were systematically investigated. Ultramicrocelluar foams with a cell size of 0.5 μm and cell density over 1012 cells/cm3 were successfully prepared. Moreover, it was observed that the system, which was strongly plasticized by CO2, would transition from foaming to crazing under certain conditions. The phenomenon was examined in detail and understood by a proposed mechanism that accounts for both homogeneous nucleation and stress fields induced crazing.
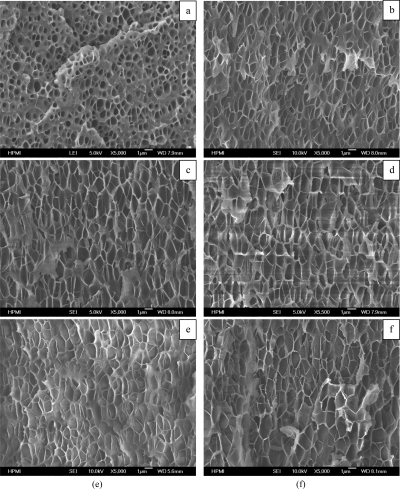
SEM micrographs of COC saturated at 7 MPa and foamed at 170 °C for various foaming times: 10 (a), 30 (b), 50 (c), 70 (d), 110 (e), and 170 s (f).
3. Kun CAO, Shui-liang WU, Shao-long QIU, Yan LI, Zhen YAO, “Synthesis of N-Alkoxy Hindered Amine Containing Si lane as a Multifunctional Flame Retardant Synergist and Its Application in Intumescent Flame Retardant Polypropylene”, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013,52: 309-317(SCI/TOP期刊)
Abstract:A novel and multifunctional flame retardant synergist, N-alkoxy hindered amine containing silane (Si-NORs), was synthesized by combining N-alkoxy hindered amine and silane coupling together through sol–gel reaction. The composition of Si-NORs was characterized by FTIR and XPS. Intumescent flame retardant polypropylene (IFR–PP) composites were prepared with different contents of Si-NOR and characterized by the limiting oxygen index (LOI), vertical burning tests (UL-94 tests), TGA, the Yellowness Index (YI), mechanical properties, and SEM measurements. The results showed that IFR–PP composites with 1 wt % Si-NORs and 25 wt % intumescent flame retardant could reach a V-0 rating in the UL-94 tests. Moreover, the thermal stability, UV stability, mechanical properties, compatibility, and char residue structure were also improved significantly, which proves Si-NOR as a multifunctional flame retardant synergist. The possible synergistic mechanism of Si-NORs was also discussed.
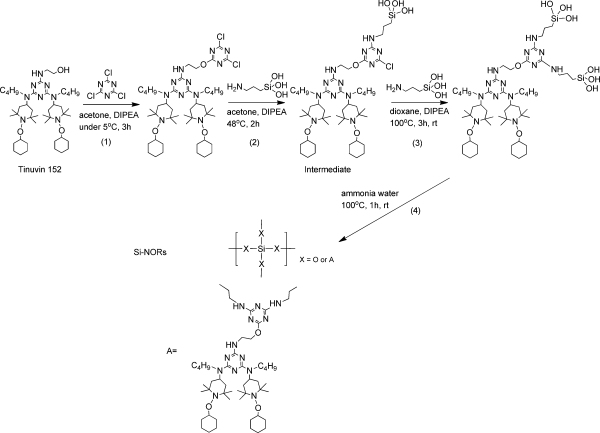
Synthetic Route for the Preparation of Si-NORs